University of Washington Workshop 2023
Note: This page is still under construction. Check back soon!
Below is an annotated agenda for the workshop. To prepare for the course, do the following steps:
1. Get Started with Matlab
Please watch this playlist for an introduction to Matlab and its basic commands; you may also want to go through the tutorials here. It is also recommended that you download version R2021a or later.
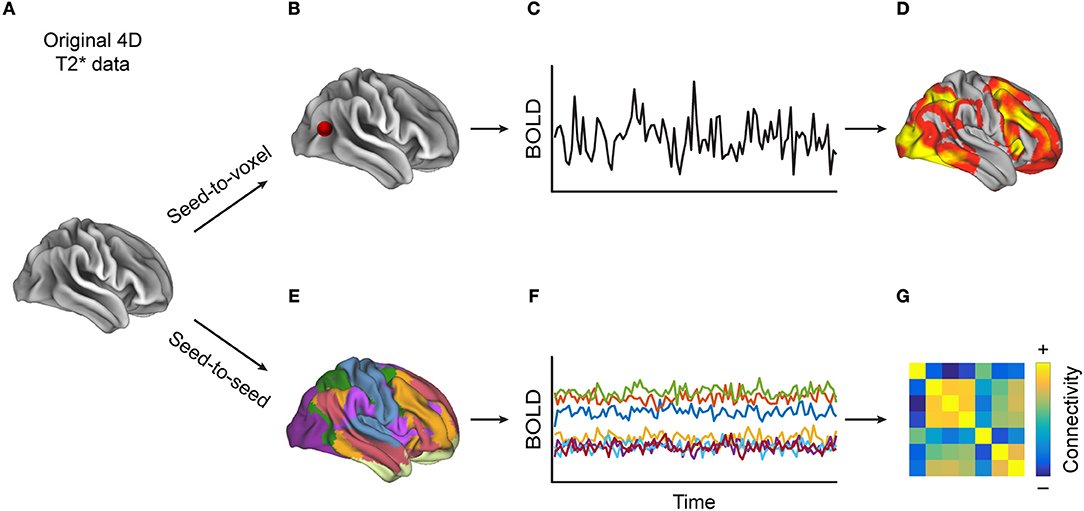
2. Install the CONN Toolbox
Use this link for instructions on how to download and install the CONN Toolbox.
Note that CONN also requires the SPM package; instructions for downloading and installing SPM can be found here.
3. Install The Decoding Toolbox
Click here to navigate to The Decoding Toolbox website; click on the link that says "click here to download TDT", and then click the download button when it takes you to a Google Drive site. Then, follow the instructions here to install and set up the toolbox.
You can also download a sample functional connectivity image here.
Day 1: Resting-State Fundamentals
Agenda
(10:00am-11:00am) Review of Matlab
This will be a brief review of Matlab and its fundamentals; these will be necessary for using the CONN toolbox, as well as more advanced methods such as scripting analyses. This lecture will cover:
Basics of navigation
Variables and Structures
Paths and Functions
Control Structures
Checking installation of SPM12; creating template job and loading it from the Matlab terminal.
(11:00am-12:30am) Introduction to Functional Connectivity and the CONN Toolbox (Lecture & Practical)
This first practical will be a guided hands-on tutorial about how to open the CONN GUI and examine some of its features. We will review the following topics:
History of functional connectivity: Landmark studies, common issues with functional connectivity, uses and future potential
Functional vs. effective connectivity
Basics of functional connectivity: Scrubbing, ROIs, correlations between regions
The debate over Global Signal Regression, and other options you can change in your analysis
Overview of the CONN GUI
Creating a new project and loading the data
Initial quality checks
(12:30pm-1:30pm) LUNCH BREAK
(1:30pm-2:30pm) Preprocessing the Individual Subject (Practical)
This practical will show how to preprocess the data for a single subject in CONN.
Realignment, slice-timing, and outlier detection
Loading the SPM.mat file
Data denoising and detrending
Checking normalization and smoothing
Quality Assurance Checks: Alignment, outlier counts, and detection
(2:30pm-3:30pm) 1st-Level Analysis and Group-Level Analysis (Practical)
As with all neuroimaging data, quality assurance checks are very important. After reviewing some common examples of quality failures, you will examine your own data.
Checking registration between T1 and T2 modalities
Alignment of the outline of the brain vs. alignment of internal structures
Outlier counts and detection
Examining the results for a single subject
Setting up group-level analyses in CONN
Second-level covariates and between-subject factors
Correction mechanisms: FWE, FDR, and cluster-forming thresholds
Exporting data for use in other packages
(3:30pm-5:00pm) Individual Consultation Sessions
Day 2: Functional Connectivity: Practice with the CONN Toolbox and Advanced Options
Agenda
(9:00am-9:45am) Review of Graph Theory (Lecture)
We begin the second half of our connectivity workshop with a brief overview of graph theory. Graph theory is closely related to the correlations between different brain regions. This lecture will cover the fundamentals you will need to understand the basic terms. In addition, we will apply this to the group-level results generated during the previous day, and learn how to interpret more advanced results.
Background of graph theory
Basics of graph theory: Nodes, edges, modularity,
Community detection
Correlation matrices and clinical applications
(9:45am-10:30pm) Setting up a General PsychoPhysiological Interaction (gPPI)
The COON toolbox is also able to do task-based connectivity through a method known as PPI. We will demonstrate how to set up a generalized PPI (gPPI) analysis for a single subject. A custom atlas and covariate files can be found here.
Overview of PPIs
Importing timing files
Importing atlases
Running the analysis and interpreting the results
(10:30am-12:00pm) Dynamic Connectivity and Surface-Based Connectivity
Dynamic connectivity measures temporal variability in functional connectivity. The most popular method is sliding-window analysis, which uses smaller intervals to measure connectivity changes over time. We will also learn about dyn-ICA, an independent components technique to identify networks that show similar temporal variations in functional connectivity.
Introduction to dynamic connectivity
Sliding-window analysis
How to set up a dyn-ICA analysis
Importing surface data output from FreeSurfer for surface-based analysis
Interpreting the results
(12:00pm-1:00pm) LUNCH BREAK
(1:00pm) Group Photo
(1:00pm-1:30pm) Scripting your analysis
Automating analyses is an indispensable skill for the neuroimaging researcher. This practical will demonstrate how to script analyses in the CONN toolbox, which can speed up processing and reduce the likelihood of error. A template script can be downloaded here.
Creating your analysis script
Looping your analysis over subjects
How to obtain converted correlation-to-z values in a Matlab structure
(1:30pm-3:00pm) Analyzing a New Dataset (Practical)
The concepts and tools we have discussed so far should provide you with enough knowledge to begin to analyze your own data. This session will be devoted to beginning your own analysis with CONN. This can either be your own data, or a dataset downloaded from an online repository, such as humanconnectome.org or openneuro.org.
As a group, we will select an open-access dataset to analyze (options will be provided by Andy). We will then determine how to analyze the dataset, and begin the processing of a single subject.
(3:00pm-3:45pm) Individual Consulting Sessions
Andy will help individuals (or small groups of individuals) with their data, from 3:00pm-3:45pm.
Day 3: Machine Learning & the Decoding Toolbox
Agenda
(9:00am-10:00am) Basics of Machine Learning (Lecture)
This session will provide an overview of MVPA, a popular multivariate tool for neuroimaging data.
Overview of Machine Learning and hyperplanes
Uses of MVPA
Experimental design considerations for studies that will use MVPA: Timing schemes, masks, and how to validate the results
(10:00am-12:00pm) Introduction to The Decoding Toolbox (Lecture & Practical)
We begin our first practical session of machine learning by using The Decoding Toolbox, a popular software program for machine learning analysis.
Overview of The Decoding Toolbox
ROI analysis vs. Searchlight analysis: Pros and cons of each
Confusion Matrices
Replicating the results from Haxby et al. (2001)
Non-parametric testing for significance
(12:00pm-1:00pm) LUNCH BREAK
(1:00pm-1:30pm) Informal Discussion with Graduate Students: Alternative Career Paths
(1:30pm-2:30pm) Representational Similarity Analysis
Representational similarity analysis (RSA) exploits the correlation similarity structure of voxels, using different distance metrics to illustrate the representational distance of different conditions.
Measurement of both content and format of representations
How this is used across modalities
Editing The Decoding Toolbox template scripts for RSA
Analysis of sample dataset
(2:30pm-3:30pm) Hyperalignment
Hyperalignment is a relatively new classification technique developed by Jim Haxby’s lab, which aligns subjects' brain data in a high-dimensional space of voxels/features.
Introduction to hyperalignment
Benefits of hyperalignment vs. traditional MVPA: Alignment of functional topographies
Hybrid hyperalignment: Combining task and functional connectivity profiles
Analysis of movie datasets: Classifying which part of a movie a subject was watching
Application to other datasets
(3:30pm-5:00pm) Individual Consultation Sessions